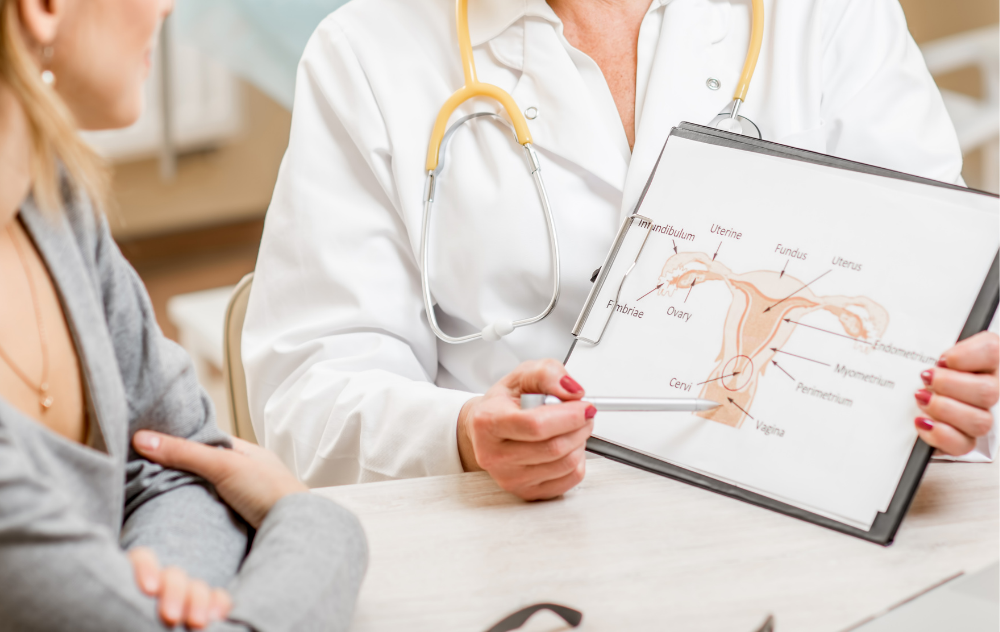
One of the most common questions patients ask is: How fast do fibroids grow? The answer depends on several factors, including age, hormones, genetics, and overall health.
Understanding Fibroid Growth
Fibroids can grow slowly or rapidly, or sometimes not at all. In some cases, they may even shrink on their own, especially after menopause. However, during a woman’s reproductive years—especially between ages 30 and 50—fibroids are more likely to grow due to higher levels of estrogen and progesterone.
Typical Growth Patterns:
-
Slow Growth: Many fibroids grow at a steady but slow pace, increasing in size by a few millimeters to centimeters over several months or years.
-
Rapid Growth: Some fibroids can double in size within a few months, particularly during pregnancy or with certain hormone therapies.
-
No Growth or Shrinking: Postmenopausal women may experience shrinking fibroids due to the natural decline in hormone levels.
What Causes Uterine Fibroids to Grow
Fibroids grow because they receive hormones through the artery they attach to. Hormones can lead to fibroid growth, so they form after puberty and often stop growing after menopause.
When hormone levels increase, fibroids may have a growth spurt during pregnancy. Fibroids have more estrogen and progesterone receptors than other cells in the uterus, which leads scientists to believe that these hormones directly impact the development of fibroids.
Insulin-like Growth Factor (IGF) is found naturally in your body and is known to stimulate the growth of cells. Many experts believe it also causes fibroids to grow.
When Rapid Fibroid Growth Becomes a Concern
While most fibroids are benign and grow slowly, sudden or fast growth should be evaluated by a doctor. This could indicate complications such as:
-
Degeneration: Rapid growth can outpace the fibroid’s blood supply, causing pain and degeneration.
-
Bulk Symptoms: Larger fibroids can cause pressure on the bladder or bowel, leading to frequent urination or constipation.
-
Unusual Cases: Although rare, extremely fast growth could be a sign of a rare cancerous tumor called a leiomyosarcoma. This is why regular monitoring is important.
Symptoms of Fibroids Growing
As fibroids grow, they can begin causing issues with the uterus and surrounding organs. You may feel a fullness or pressure in your abdomen as the fibroids get larger. If they start to press on the bladder or bowels, you may experience increased frequency of urination and constipation.
Another way to tell fibroids are growing is if your stomach increases in size. As the fibroids get larger, they can cause a distended stomach as if you have gained weight or are pregnant.
How Fast Can Fibroids Grow?
Unfortunately, there’s no simple answer to “how fast do fibroids grow over time.” The rate of fibroid growth is often unpredictable, which can be challenging and frustrating. For many women, growth is slow and doesn’t involve any significant increase of symptoms. Some women have fibroids that remain stable for many years.
For others, fibroid growth can be rapid and accompanied by debilitating, life-altering effects like heavy bleeding, severe pelvic pain, and a visibly enlarged abdomen. Alternatively, there are times when fibroids tend to shrink, such as after pregnancy or menopause. This can bring about a reduction of related symptoms.
At USA Fibroid Centers, we are committed to educating women on uterine fibroids and their full range of fibroid treatment options. When it comes to fibroid growth, the most important thing to understand is that treatment is recommended based on bothersome symptoms, not actual size.
Generally speaking, when uterine fibroid growth impacts your career, relationships, self-esteem, or ability to perform daily tasks, you may want to explore your treatment options. If you are experiencing new or worsening fibroid symptoms, we urge you to contact a fibroid specialist for full medical evaluation.
What Is Considered a Fast-Growing Fibroid?
Along with wondering how fast fibroids grow, you may also be curious about what is considered a fast-growing fibroid. A research study revealed that the average growth is 89% over 18 months. As a point of reference, a two-centimeter fibroid – about the size of a blueberry – is likely to take four to five years to double its diameter. This same study also suggests that very small fibroids grow more quickly than larger ones.
If your fibroid is expanding quicker than average, it may be classified a fast-growing fibroid. At USA Fibroid Centers, we know that larger fibroids (or multiple fibroids) are more likely to cause problematic symptoms that require intervention. In other words, it is the resulting fibroid size and number of tumors that impact the quality of life.
How Do I Know if My Fibroids Are Growing?
The only surefire way to know if your fibroids are growing is to undergo an ultrasound or MRI exam. If you visit a fibroid specialist, they will likely order medical imaging when you experience increased symptoms, such as heavier bleeding or more pain than usual. Increased uterine fibroid symptoms can be strong indicators of underlying fibroid growth.
Keep in mind that fibroid symptoms can resemble those of other health conditions of the reproductive tract. Some of these can be serious and potentially life-threatening. Changes in a women’s monthly cycle always require medical evaluation.
Can Fibroids Grow in Six Months?
Fibroids can grow within six months but may not be detectable. Some fibroids won’t show any symptoms during that time, while others may increase enough in size to affect your well-being.
You may look like you’ve gained weight or are pregnant as they grow. Others may start to press on organs as they grow even though the change isn’t detectable on the outside. Changes in hormone levels can also cause fibroids to grow more rapidly, such as when you’re pregnant or begin taking birth control pills.
Fibroid Treatment
We recommend contacting your doctor or a fibroid specialist if you’ve noticed any changes in:
- Menstrual bleeding
- Pelvic pain
- Rate of urination
- Abdominal size
- Energy levels
- Comfort during sex
- Other fibroid symptoms
We offer a minimally-invasive, non-surgical fibroid treatment called Uterine Fibroid Embolization (UFE). UFE can eliminate your fibroids, relieve related symptoms and quickly get you back to normal life.
UFE is an outpatient procedure that allows the interventional radiologist to locate the fibroid through ultrasound technology. They will insert a tiny catheter into the thigh or wrist and inject embolic materials into the artery which is attached to the fibroid. Once the blood flow is restricted, the fibroid can no longer receive nutrients, causing it to shrink and die.
When comparing a hysterectomy vs. UFE, it’s important to understand that UFE preserves your fertility by leaving the uterus intact. UFE also has a much shorter recovery time of typically one to two weeks, while a hysterectomy often takes up to eight weeks to resume normal activities.
Contact USA Fibroid Centers
Fibroids don’t grow at the same rate for every woman, and there’s no one-size-fits-all timeline. Whether they remain small for years or grow quickly in just a few months, staying informed and working with a specialist can help you make the best decisions for your health.
Because we believe in convenient access to fibroid care, we offer dozens of clinic locations nationwide. To get started, schedule an initial consultation online or call us at 855.615.2555.