Vaginal bleeding outside of your regular menstruation cycle may be referred to as intermenstrual bleeding or spotting. It is possible for spotting to occur at any age after puberty and can be caused by different conditions, such as fibroids or even pregnancy. Sometimes, women may even experience spotting during ovulation due to a sharp decrease in estrogen.
As a result, it’s essential to understand what vaginal spotting looks like and the possible causes. If you are experiencing spotting, it is important to see your doctor to rule out any underlying medical conditions.
In most cases, light spotting does not require treatment. However, monitoring your symptoms and letting your doctor know if you experience any other unusual changes is advised.
SCHEDULE A HEALTH CONSULTATION TODAY
What is Spotting?
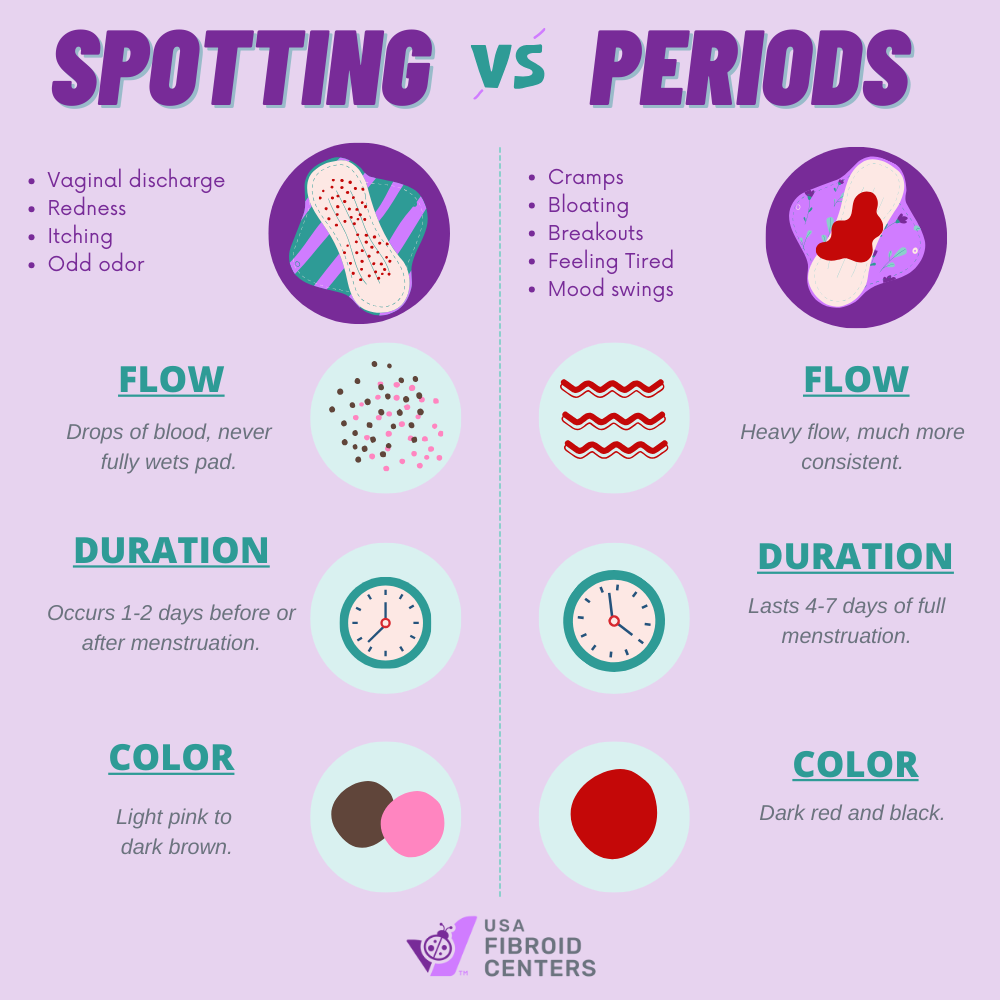
Spotting is light vaginal bleeding that occurs outside of your regular menstrual cycle. It is usually lighter than your regular period and may not require a tampon or pad. The color of the blood from spotting can range from light pink to dark brown but is commonly a lighter red color.
It is possible to identify spotting by color, consistency, and amount. These characteristics help distinguish spotting from other types of bleeding and recognize when to consult your healthcare provider.
Spotting vs. Period: What’s the Difference?
It is easy to confuse menstrual bleeding with spotting, especially if you have lighter periods. However, there are a few differences between the amount of blood and the duration, flow, color, and other indicators.
Spotting can occur just before or after your period. Spotting before a period is usually due to the initial breakdown of the uterine lining, resulting in a small amount of blood.
After a period, the expulsion of the remaining uterine lining that is not fully shed during menstruation may cause spotting. This type of spotting is light and ranges in color from light pink to dark brown, depending on how long the blood has been in the body.
Light Flow vs. Spotting
Spotting is typically defined as vaginal bleeding that is less than 2 tablespoons (30 milliliters) per day. A period is a more significant amount of vaginal bleeding, normally lasting for 3-7 days. It may be light or heavy, but there should be enough blood to soak through a pad or tampon every few hours.
Why am I Spotting?
The best way to determine what’s causing spotting is to monitor any accompanying symptoms. There are a few common conditions that can cause vaginal spotting, including uterine fibroids, hormone changes, and pregnancy.
Spotting Due to Fibroids
Spotting is a common symptom of uterine fibroids, which are noncancerous growths in the uterus. Fibroid symptoms include heavy or irregular menstruation, pelvic pain or pressure, frequent urination, a diminished sex drive, and low energy levels. Women often develop fibroids during their reproductive years, with up to 80% affected by age 50. Despite their prevalence, many women are unaware they have fibroids until they become symptomatic.
Fibroids can cause vaginal spotting, as well as heavier bleeding during periods, in several ways:
- They can distort the shape of the uterine cavity, making it more difficult for the uterus to shed its lining during menstruation.
- Fibroids can increase the production of blood vessels in the uterus.
- Some fibroids may also produce hormones that can stimulate the uterine lining.
If you think uterine fibroids may be causing your spotting symptoms, contact us today at 855.615.2555 to discuss all your treatment options.
CALL TO SCHEDULE A FIBROID CONSULTATION
Spotting Due to Hormonal Changes
Spotting caused by hormone changes is not uncommon. While it can occur at any age, it happens often during puberty, perimenopause, and menopause. Hormonal changes can cause spotting by affecting the way the lining of the uterus builds up and sheds its lining.
Some common causes of vaginal spotting from hormone changes include:
- Ovulation: Mid-cycle spotting, also known as ovulation spotting, is a light bleeding occurring around ovulation. It is usually caused by a drop in estrogen levels. Spotting during ovulation is usually harmless and does not require treatment.
- Birth control: Birth control pills, implants, and other hormonal contraceptives can cause spotting, especially when you first start using them. This is because your body is adjusting to the new hormones. Spotting caused by birth control usually goes away within a few months.
- Perimenopause and menopause: During perimenopause and menopause, your hormone levels fluctuate. This can cause spotting, irregular periods, and other menstrual changes. Spotting caused by perimenopause and menopause is usually not harmful and does not require treatment.
Spotting During Pregnancy
Another reason women may experience spotting is because of pregnancy. Vaginal spotting can happen at any time during pregnancy, but it is most common in the first trimester.
One common cause of spotting during pregnancy is implantation, which occurs when the fertilized egg attaches to the uterine lining. Implantation bleeding is usually light and occurs around 6-12 days after conception. It may only last for a few hours or days. Many pregnant women may also notice light traces of pink, red, or dark red blood.
Vaginal bleeding during pregnancy has many causes, some serious, some not. However, while bleeding in early pregnancy is common, it is more serious in later stages.
Track any spotting you experience during pregnancy, including the amount and color. If you lose more than two tablespoons (30 milliliters) of blood daily, you should consult your doctor immediately. Additionally, it’s important to note other symptoms accompanying the spotting, such as cramping or pain.
Spotting and Birth Control
Spotting is common when initiating birth control, primarily due to the fluctuation in hormone levels affecting the stability of the uterine lining. According to the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG), low-dose birth control pills, implants, and hormonal IUDs are the primary culprits for causing spotting.¹
Factors such as smoking, irregular pill consumption, or continuous pill usage to skip periods can also contribute to spotting, along with emergency contraceptives, like the morning-after pill.
This spotting can occur when it is your first time using hormonal birth control, switching between different forms, or moving from hormonal to non-hormonal birth control. Typically, it may look like period blood or blood mixed with normal vaginal discharge.
Birth control spotting happens intermittently until your body adjusts to the hormone levels within the first three months. Other side effects during this adjustment period can include irregular periods, cramping, headaches, and nausea.
If spotting persists beyond a few months or occurs alongside other symptoms, contact a healthcare professional to determine if the spotting results from an underlying issue.
Spotting and Menstrual Cycle
Spotting can occur at different times throughout the menstrual cycle because of hormone changes, including ovulation. Ovulation is around the midpoint of a 28-day cycle when one of your ovaries releases an egg. Just before ovulation, your estrogen levels rise, preparing the lining of your uterus for a potential pregnancy.
If conception does not occur, estrogen levels drop, which can cause light bleeding or discharge that is pink or brown. Spotting during ovulation usually continues until hormone levels stabilize, typically within a few days.
Tracking your menstrual cycle helps you identify spotting patterns and understand when it might be a regular part of your cycle or a potential issue. Recording the timing, color, and amount of spotting, along with accompanying symptoms such as cramping or changes in discharge, is valuable information for your healthcare provider if you notice anything unusual.
Spotting Due to Medical Conditions
Spotting can be a symptom of various medical conditions and sexually transmitted infections (STIs), often accompanied by other signs such as vaginal discharge, redness, itching, or an unusual odor. STIs like gonorrhea and chlamydia can cause spotting between periods, along with changes in discharge appearance and smell, fever, pain during urination, pain during sex, and itching around the vulva.
Untreated STIs can worsen and lead to complications like pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) and future pregnancy difficulties. Testing for STIs and treating them is essential for reproductive health, especially as many STIs are easily treatable with antibiotics.
Besides STIs, spotting can also result from medical conditions, including the following:
If you experience spotting along with other symptoms, seeking help from medical professionals for early diagnosis and treatment can prevent reproductive health complications.
Healthcare providers can perform tests, including STI screenings, ultrasounds, and blood tests, to determine the cause of the spotting and recommend appropriate treatment. Regular check-ups, pap smears, and open communication with your doctor are key to effectively managing your health.
At USA Fibroid Center, our fibroid specialists can help you determine if fibroids or another medical condition are causing your spotting and devise the best treatment plan for you.
How to Manage Spotting
For many, spotting will resolve without medical intervention, so maintaining a healthy lifestyle, managing stress, wearing panty liners when needed, and tracking your menstrual cycle is usually enough. Over-the-counter medications such as pain relievers are also suitable for managing any discomfort or mild cramping caused by the spotting.
If spotting persists longer than a few months, consult a healthcare professional. Treatments for underlying causes of spotting, including infections, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), polyps, and fibroids, usually require medical intervention.
You should see a doctor if you notice any changes in your cycle, such as persistent spotting or longer, shorter, or more painful periods. However, immediate medical attention is necessary if you experience:
- Persistent spotting or bleeding after sex
- Frequent spotting or bleeding between periods
- Spotting that doesn’t turn into a regular period
- Green, yellow, thick, or clumpy vaginal discharge
- Strong vaginal odor or change in vulva smell
- Redness, itching, burning, or irritation around the vulva
- Pain during urination or sex
- Lower abdominal or pelvic pain
- Fever higher than 100.4°F
When consulting with your doctor, keep a detailed personal and family health history, track your spotting, and bring a list of all your medications. A thorough history, pelvic examination, pregnancy test, Pap smear, blood or urine tests, and imaging studies such as ultrasounds may be necessary for diagnosis.
If your spotting is a result of fibroids, treating them through procedures such as uterine fibroid embolization can help minimize or stop the spotting.
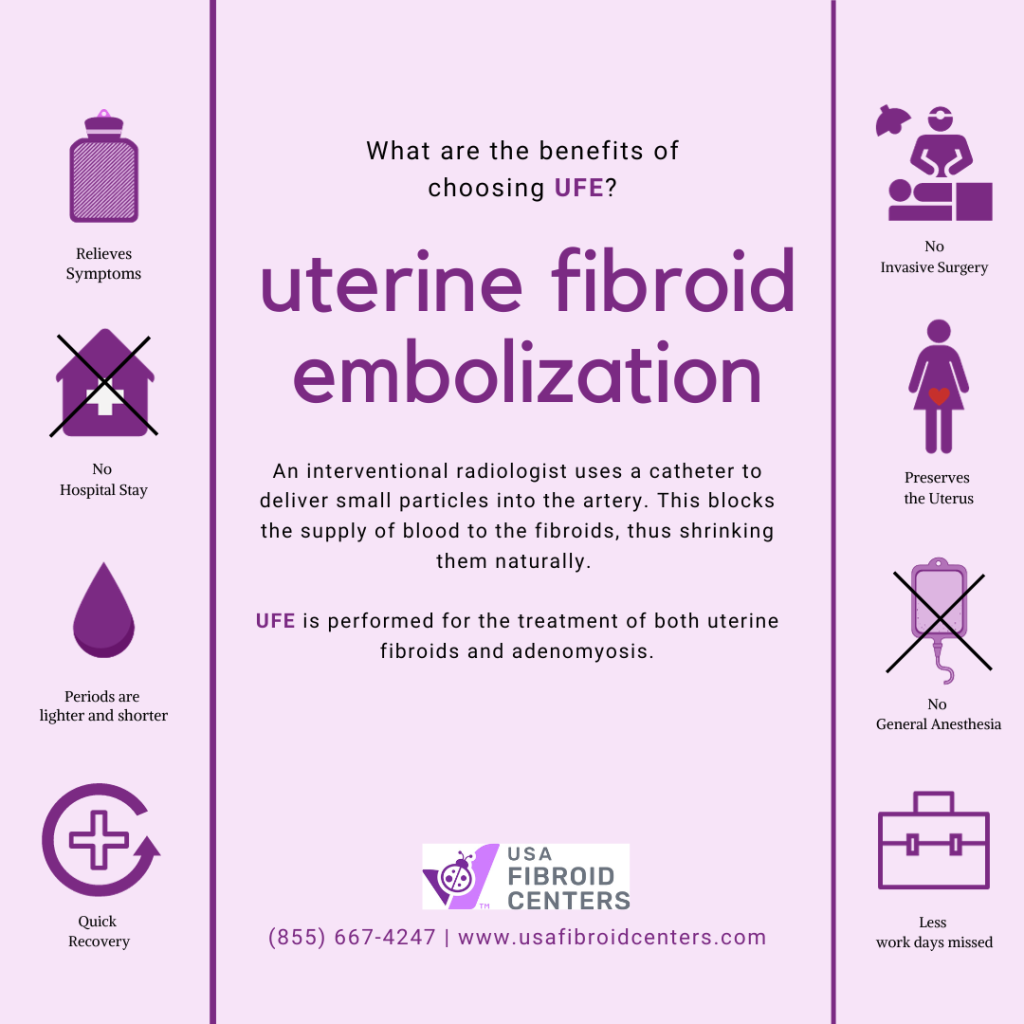
Treating Spotting Related to Fibroids With Uterine Fibroid Embolization (UFE)
Uterine Fibroid Embolization (UFE) is a minimally invasive procedure for fibroids that involves blocking their blood supply, so the fibroids shrink and die. UFE can help relieve symptoms such as heavy bleeding, bleeding between cycles, frequent urination, painful sex, and pelvic pain
UFE offers many benefits to patients seeking alternatives to a hysterectomy or myomectomy. This non-surgical procedure uses imaging guidance to insert a thin, flexible tube called a catheter into an artery in the groin or wrist.
The doctor uses real-time X-rays to precisely position the catheter and then injects tiny particles that block the blood flow to the fibroids. By cutting off their blood supply, the fibroids shrink and eventually die off.
If you are concerned that you have fibroids, are dealing with spotting, and want to learn more about treatment options before or after pregnancy, schedule a consultation at USA Fibroid Centers today.
SCHEDULE ONLINE AT A LOCATION NEAR YOU
FAQs
What Color is Blood During Spotting?
Vaginal spotting can appear in various colors, depending on factors such as how long it takes to leave your body, possible infections, and if it is mixed with other fluids. Spotting is most commonly a lighter or darker hue of red. If you have an infection, and the blood is mixed with vaginal discharge, it may be a pink or orange color. Older blood that oxidizes will appear brown.
What Does Spotting Mean?
Spotting can result from factors such as hormone changes, sexually transmitted infections (STIs), and fibroids. In some cases, it can even be caused by implantation bleeding from pregnancy. Since there are many reasons for spotting, it’s important to note any other symptoms you might be experiencing.
How Long Does Spotting Last?
How long vaginal spotting occurs depends on what is causing it. However, spotting can typically last anywhere from a few days to weeks.
How can I tell if I’m having a Light Period vs. Spotting?
The amount of blood lost during spotting can vary from person to person. It is usually less than two tablespoons (30 milliliters). Light spotting can be as little as minor drops of blood on your underwear or toilet paper. In other cases, spotting may be heavier, but it should still be less than a regular menstrual period. When a panty liner or pad is needed to manage a heavy blood flow and prevent leakage, it is a period.
What does Pregnancy Spotting Look Like?
The American Pregnancy Association reports that approximately 20 to 30 percent of women experience bleeding in early pregnancy.² Light bleeding or spotting during the first trimester can occur around 1 to 2 weeks after fertilization because of implantation bleeding.³ The cervix may become irritated during the second trimester, typically after intercourse or a cervical exam, leading to light bleeding or spotting.
Some signs of implantation bleeding during pregnancy include:
- Spotting occurs 6-12 days after conception. Any spotting before or after this time frame is more likely caused by something else.
- Implantation bleeding is typically light and does not soak through a pad or tampon.
- It is pink, brown, or light red, unlike menstrual bleeding, which is bright red.
- Implantation bleeding may be accompanied by mild cramping, but it is not usually severe.
Talk to your doctor if you have any concerns about spotting in early pregnancy so they can help you determine the cause of the bleeding and provide appropriate care. If you have fibroids and experience unusual bleeding, it is important to understand the risk factors fibroids pose in pregnancy.
STILL HAVE QUESTIONS? CONTACT US TODAY
Sources
- Valerie French, “What You Should Know About Breakthrough Bleeding with Birth Control,” ACOG, January 2021.
- “Bleeding During Pregnancy,” American Pregnancy Association, February 14, 2022.
- “Bleeding During Pregnancy,” ACOG, August 2022.