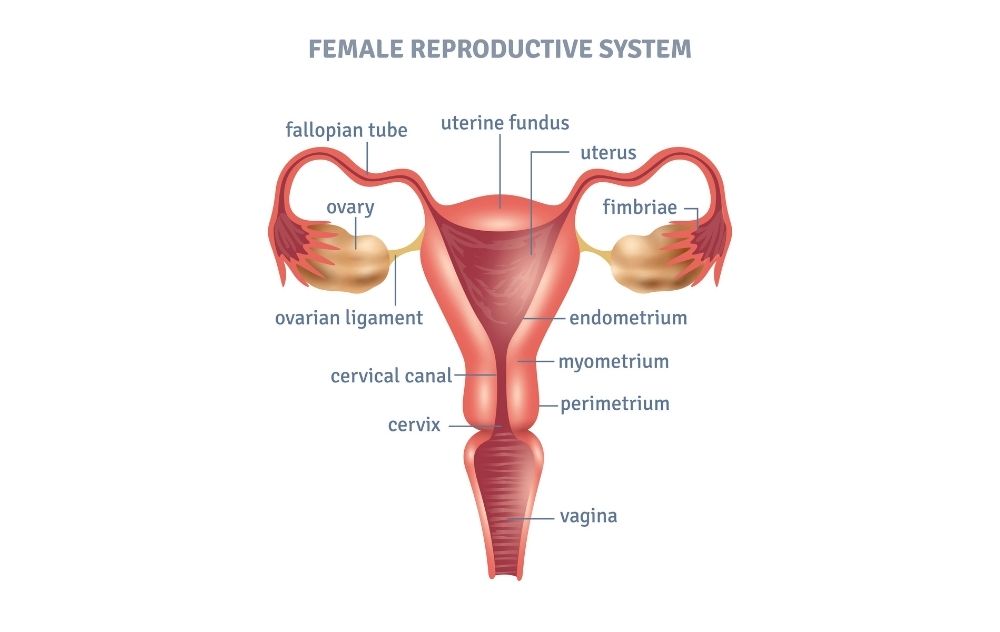
When it comes to understanding female reproductive anatomy, most people are familiar with terms like “uterus,” “ovaries,” and “fallopian tubes.” But what about the fundus of the uterus? Though it may sound like a complicated medical term, the fundus plays an important role in both pregnancy and general reproductive health.
What is the Fundus of Uterus?
The fundus is the top portion of the uterus, opposite the cervix. It’s the rounded, dome-like area above where the fallopian tubes connect to the uterus. If you imagine the uterus as an upside-down pear, the fundus would be the broadest, uppermost part.
Where is the Fundus of Uterus?
The fundus of the uterus is located at the top of the uterus and across from the cervix. The cervix is the opening into the uterus from the vagina.
Different Parts of the Fundus of Uterus
The fundus of the uterus has three layers, just like the rest of the uterus.
- Perimetrium, which covers from the outside of the organ.
- Myometrium, which is the second and muscular layer.
- Endometrium, which is the inner lane and mucous membrane.
What Does the Fundus Do?
While the fundus doesn’t have a unique function separate from the uterus, its location and structure play key roles in several reproductive processes:
1. Pregnancy Monitoring
During pregnancy, the fundus becomes an important measurement point. Healthcare providers often measure fundal height — the distance from the pubic bone to the top of the uterus — to assess fetal growth and estimate gestational age.
2. Contractions and Labor
The fundus is involved in uterine contractions. During labor, contractions often begin in the fundus and move downward to help push the baby out.
3. Placenta Position
The fundal region may be the site where the placenta attaches. A “fundal placenta” simply means the placenta is located at the top of the uterus, which is a common and healthy position.
Common Conditions Affecting the Fundus
Several conditions can affect the uterine fundus. Uterine fibroids are among the most common — these benign tumors can grow in the fundal area which is located near the top of uterus – leading to heavy bleeding, pelvic pain, or fertility issues. Large fundal fibroids may also complicate pregnancy by altering the shape of the uterus. Adenomyosis, where endometrial tissue grows into the uterine muscle, can thicken and tenderize the fundus, often causing painful, heavy periods. Congenital malformations, such as a bicornuate uterus, may change the fundus’s shape and impact fertility. In rare cases, excessive fundal pressure during labor may pose risks, especially in complicated pregnancies.
Average Size and Weight of Uterus
Fundus of Uterus and Fibroids
When fibroids develop in the fundus of the uterus, they are often referred to as fundal fibroids. Located at the top portion of the uterus, these growths can range in size and may be either embedded in the muscular wall (intramural) or project into the uterine cavity (submucosal) or outward (subserosal). Fundal fibroids can cause a variety of symptoms, including heavy menstrual bleeding, pelvic pressure, and lower back pain. In some cases, they may interfere with fertility or complicate pregnancy by distorting the uterine shape or affecting embryo implantation. Because of their location, large fundal fibroids may also impact the accuracy of fundal height measurements during pregnancy. Early diagnosis and treatment, such as Uterine Fibroid Embolization (UFE), can help manage symptoms and preserve the uterus without surgery.
You may not know you have fibroids or suffer from any symptoms, especially if they are small. However, these fibroids may grow as they receive nutrients through the blood flow of the artery they are attached to, increasing the likelihood that they may disrupt your life and cause discomfort. If you experience any symptoms, they may include:
- Heavy periods
- Bleeding between periods
- Pelvic pain or low back pain
- Abdominal pain or severe cramping
- Anemia
- Fatigue
You may also notice an enlarged uterus as the fibroids take up more space, making you look like you have gained weight. If you experience any of these symptoms or suspect you have fibroids, you should seek diagnosis and treatment.
Contact USA Fibroid Centers
USA Fibroid Centers provide minimally invasive treatment for uterine fibroids through uterine fibroid embolization (UFE). UFE is a minimally invasive treatment that may shrink the fibroids, alleviating any symptoms you experience. We can help you find relief and start enjoying a higher quality of life again. Schedule a consultation online to learn more or call us at 855-655-2555 to visit one of our facilities.