Uterine fibroids are common, noncancerous growths that develop in or around the uterus. Many women may struggle with heavy periods, pelvic pain, or fertility challenges due fibroids. The size and location of fibroids play a crucial role in determining their impact on health.
This visual guide provides a clear understanding of fibroids by breaking down types, location, size, diagnosis and treatment options for those who want a clear understanding of uterine fibroids.
If you have any concerns, we recommend scheduling a consultation online today to get the help you deserve.
Schedule a Consultation Online Today
What are Uterine Fibroids?
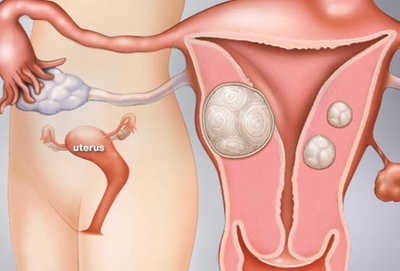
Uterine fibroids are benign tumors that grow from the walls of the uterus. The medical terms for these fibroids are “leiomyoma” or “myoma.” There is no specific known cause of uterine fibroids, although age, race, genetics, and hormonal fluctuations are thought to be some of the main contributing factors. Uterine fibroid tumors are not unusual; in fact, they affect roughly one-third of all women under age 50. There are different kinds of uterine fibroids, and their size, location, and number can all influence whether a woman will experience fibroid symptoms.
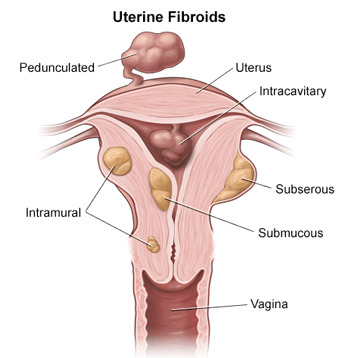
Fibroid Types and Locations
Here are four common types of uterine fibroid tumors:
Intramural Fibroids: These fibroids grow in the walls of the uterus and they are the most common type of fibroids. When an intramural fibroid tumor expands, it tends to make the uterus feel larger than normal, which can sometimes be mistaken for pregnancy.
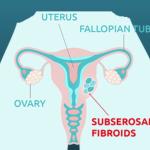
Subserosal Fibroids: These fibroids grow outside the uterine lining. As this type of fibroid continues to grow outward, it can increase in size. If a subserosal fibroid tumor gets too big, it may put additional pressure on the surrounding organs.
Submucosal Fibroids: Theses fibroids grow under the uterine lining and can enter the uterine cavity, causing heavy bleeding. Large submucosal fibroid tumors may increase the size of the uterine cavity and block the fallopian tubes, which can cause complications with fertility.
Pedunculated Fibroids: These floating fibroids grow on small stalks inside or outside the uterus, meaning they can be submucosal or subserosal. Pedunculated fibroid tumors may cause pain or pressure if the fibroid twists on the stalk.
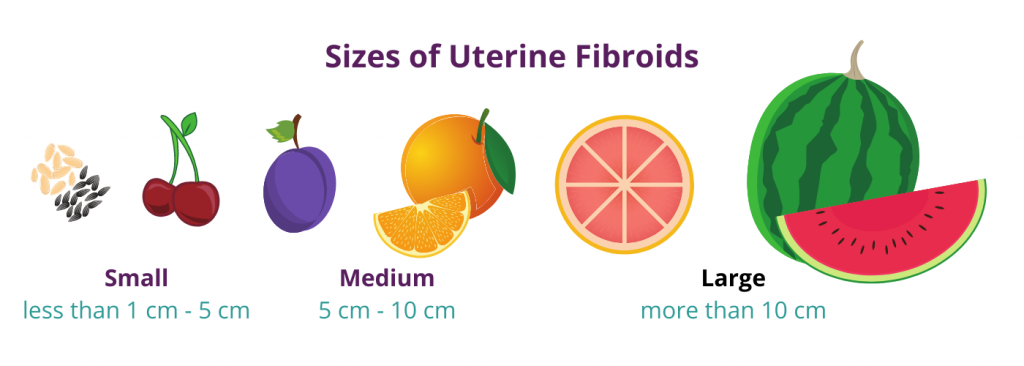
Fibroid Tumor Sizes
Fibroid tumor sizes can be grouped not just by type, but by size as well. This fibroid tumor size chart offers a helpful visual guide:
- Small: (less than 1 cm to 5 cm): Ranging in size from a seed to a cherry
- Medium: (5 cm to 10 cm): Ranging in size from a plum to an orange
- Large: (More than 10 cm): Ranging in size from a grapefruit to a watermelon
Small fibroids 1 cm and under may not cause you to experience any symptoms; however, 5 cm fibroids and larger may cause women severe pelvic pain and heavy periods. Fibroids that are closer to 10 cm and larger may cause frequent urination, constipation, and a protruding abdomen or belly.
Fibroid growth patterns can be irregular, with dormant periods followed by times when the fibroid enlarges. The largest fibroid ever reported was one that weighed more than 100 pounds when removed. Fibroids can also grow in clusters to create a large, heavy mass. Generally, if fibroids are large in size, weight, and number, there is a greater chance that they will trigger symptoms.
If your symptoms interfere with your daily life, one of our fibroid specialists can help you find relief.
Symptoms & Risks Related to Types of Fibroids
Intramural Fibroids (Most Common)
- Location: Within the muscular wall of the uterus
- Symptoms: Heavy periods, pelvic pain, frequent urination, bloating, and lower back pain
- Impact on Fertility: May affect implantation or distort the uterus
Subserosal Fibroids
- Location: On the outer wall of the uterus
- Symptoms: Pelvic pressure, bloating, back pain, and pain during intercourse
- Impact on Fertility: Rarely affects pregnancy but may cause discomfort due to pressure on other organs
Submucosal Fibroids
- Location: Inside the uterine cavity, beneath the endometrial lining
- Symptoms: Heavy menstrual bleeding, prolonged periods, anemia, and fertility issues
- Impact on Fertility: Can interfere with implantation and increase the risk of miscarriage
Pedunculated Fibroids
- Location: Attached to the uterus by a thin stalk, either inside (submucosal) or outside (subserosal)
- Symptoms: Pain, cramping, and possible torsion if the stalk twists
- Impact on Fertility: May cause discomfort but usually does not interfere with pregnancy
Fibroid Diagnosis and Treatment Options
Fibroids are typically diagnosed through a combination of medical history, physical examination, and imaging tests. A pelvic exam may reveal an enlarged or irregularly shaped uterus. Ultrasound is the primary imaging technique, using sound waves to create images of the uterus and identify the presence, size, and location of fibroids. Other imaging tests, such as MRI, may be used to obtain more detailed information, especially for larger fibroids or those located in specific areas of the uterus.
Treatment options
If you are diagnosed with fibroids, sometimes oral contraceptives are used to manage the levels of estrogen and progesterone. Birth control is a temporary method to reduce fibroid pain or heavy bleeding. Some other hormone therapies may also give temporary relief from fibroids by stopping periods.
A hysterectomy is one of the most common procedures performed for fibroids. According to the National Institutes of Health, 200,000 hysterectomies are performed in the United States every year to eliminate fibroids. Many women experience psychological and emotional issues following a hysterectomy procedure.
Another treatment option is myomectomy, which involves the surgical removal of the fibroids. Because it is a surgery, it requires a longer recovery time.
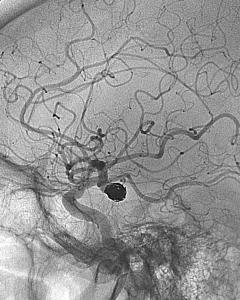
A non surgical option is Uterine Fibroid Embolization. UFE is a minimally invasive procedure that shrinks fibroids by cutting off their blood supply. It comes with the benefits of reducing symptoms, preserving the uterus, shorter recovery and can be done in an outpatient environment. UFE is our specialty and focus. Our doctors focus on determining if women are a candidate for UFE as it is effective and has less risks than an invasive option.
Contact USA Fibroid Centers
We know that uterine fibroids can be painful. We never want anyone to suffer from fibroid symptoms or wonder how they can get treatment. At USA Fibroid Centers, we specialize in a non-surgical treatment for uterine fibroids known as UFE. If you are interested in learning more about this treatment, or if you want to schedule an appointment, give us a call at 855.615.2555.
We are happy to answer any questions you may have to help you get the relief you need.