
Can fibroids grow during pregnancy? How might this affect your health or your baby’s development if they do?
Many women with uterine fibroids understandably have concerns about how pregnancy might impact these noncancerous growths and, conversely, how the fibroids might affect their pregnancy.
Our fibroid specialists at USA Fibroid Centers hear this common question: “Can fibroids grow during pregnancy?” If you are planning to get pregnant and know you have fibroids, determining if addressing your fibroids before your pregnancy is crucial.
While we specialize in Uterine Fibroid Embolization (UFE), a minimally invasive treatment option not performed during pregnancy, we understand the importance of addressing these concerns. This blog post will explore the relationship between fibroids and pregnancy, providing information about potential growth, associated risks, and management strategies.
LEARN MORE ABOUT FIBROIDS AND PREGNANCY
What Makes Fibroids Grow During Pregnancy?
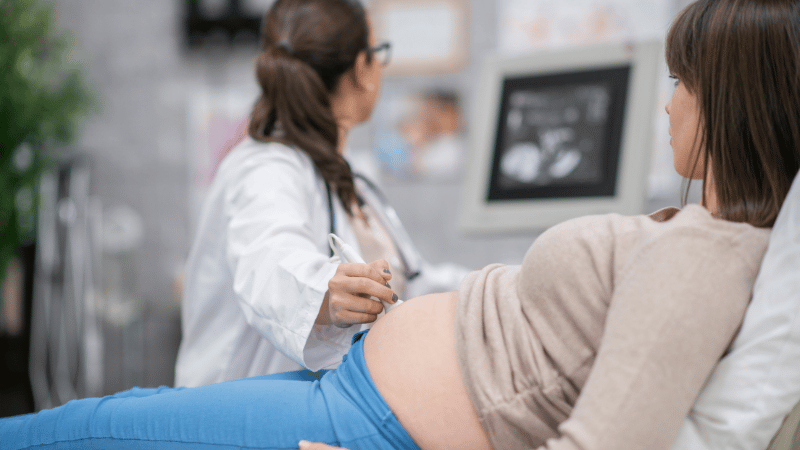
During pregnancy, the body undergoes hormonal and physical changes, which can influence the behavior of fibroids. Elevated hormone levels and increased uterine blood flow may stimulate fibroid growth.
Hormonal Influence
Higher estrogen and progesterone levels during pregnancy can fuel fibroid growth. Along with estrogen and progesterone, fluctuation, known as human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), further influences fibroid size, underlining the relationship between pregnancy hormones and fibroid growth.
Increased Blood Flow
Pregnancy causes the body to undergo significant circulatory changes to support the growing fetus. This increase in uterine blood flow gives fibroids the nutrients and oxygen needed to grow. However, the degree of growth varies depending on the fibroid’s location and size and how much uterine blood flow increases.
Fibroid Type and Location
The fibroids’ type and location impact pregnancy and overall health. These types include:
Submucosal fibroids: These fibroids grow just beneath the uterine lining (endometrium), protruding into the uterine cavity and potentially distorting its shape. This distortion can increase the risk of infertility, fetal growth restriction, and miscarriage.
Intramural fibroids: Growing within the muscular wall of the uterus, these fibroids can distort the uterine shape, impacting fetal growth and positioning depending on their size and location.
Subserosal fibroids: These fibroids develop on the outer surface of the uterus, bulging into the pelvic or abdominal cavity. While less likely to directly affect the pregnancy within the uterus, larger subserosal fibroids can cause discomfort or complications by pressing on nearby organs like the bladder or bowel.
Understanding the type and location of fibroids is essential for managing pregnancy and fibroid growth and determining the appropriate treatment options.
MEET WITH A FIBROID SPECIALIST
How Fibroids Change During Pregnancy: Size and Growth Rate

Fibroids can change significantly during pregnancy. While some fibroids grow, others remain stable or shrink, depending on various factors.
Factors that affect fibroid growth speed:
- Hormone Levels: Elevated estrogen and progesterone levels fuel fibroid development.
- Fibroid Location: Submucosal fibroids tend to have a more significant impact on pregnancy and fibroid growth.
- Uterine Blood Flow: Increased blood flow during pregnancy may nourish fibroids, encouraging growth.
- Fibroid Size: Smaller fibroids are more likely to grow during pregnancy.
- Genetics: Family history can influence how much fibroids develop during pregnancy.
- Age: Younger women may experience more fibroid growth due to higher baseline hormone levels.
- Number of Fibroids: Having multiple fibroids can compound symptoms and complications.
- Hormonal Birth Control Use: Previous use of hormonal birth control may impact fibroid development.
Growth tends to be most rapid during the first trimester when estrogen and progesterone levels surge. Studies show approximately 71.4% of fibroids grow during the first and second trimesters, and 66.6% continue to grow during the second and third trimesters.¹
How Big Can Fibroids Grow During Pregnancy?
Some fibroids may increase only a few centimeters during pregnancy, while others grow substantially, sometimes doubling within the first few weeks.² The size of a fibroid can impact pregnancy symptoms, such as larger fibroids potentially causing pelvic pain, pressure, or complications during delivery.
To better understand the implications during pregnancy, fibroids are categorized by size:
| Size | Measurement | Potential Complications |
| Small Fibroids | Less than 5 cm | Minimal symptoms and a lower risk of pregnancy complications. |
| Medium Fibroids | 5–10 cm | Mild to moderate pelvic pain or pressure. |
| Large Fibroids | Greater than 10 cm | There is a higher risk of symptoms and delivery complications. |
Understanding the possible changes in fibroid growth and their implications can help you and your healthcare team manage fibroid-related challenges during pregnancy.
CALL 855.615.2555 FOR MORE INFORMATION
How to Prevent Fibroids From Growing During Pregnancy
While fibroid growth during pregnancy cannot always be prevented, proactive management can help reduce its impact.
Regular prenatal care is essential for managing pregnancy and fibroid growth, which can include:
- Frequent ultrasounds to track fibroid size and growth.
- Assessment of potential complications such as pain, bleeding, or changes in fetal development.
- Monitoring specific fibroid symptoms, such as increased pelvic pressure or urinary frequency.
If you’re planning a pregnancy and have concerns about fibroids, schedule a consultation with a fibroid specialist at USA Fibroid Centers. We can help you understand your options and develop a personalized plan to manage your fibroids before you conceive. While we don’t perform UFE during pregnancy, addressing fibroids beforehand can significantly improve your chances of a healthy pregnancy.
Managing Fibroid Growth During Pregnancy

Fibroid growth during pregnancy is a common concern, but its impact depends on fibroid size, location, and hormone levels. Frequent check-ups and ultrasounds allow healthcare providers to track fibroid changes, address symptoms, and alleviate potential complications for the best outcomes for you and your baby.
Our fibroid specialists at USA Fibroid Centers can help you navigate the challenges of pregnancy and fibroid growth with personalized treatment, such as uterine fibroid embolization (UFE).
Frequently Asked Questions
Is it Normal for Fibroids to Grow During Pregnancy?
Hormonal and physical changes during pregnancy can influence fibroid growth. Increased estrogen, progesterone, and uterine blood flow cause fibroids to grow.
How Do Fibroids Grow During Pregnancy?
During pregnancy, factors such as hormone levels, fibroid size, genetics, age, and prior use of hormonal birth control can influence fibroid growth.
How Fast Do Fibroids Grow During Pregnancy?
Fibroid growth tends to be most rapid during the first trimester when hormone levels surge, with studies showing significant growth in 71.4% of fibroids during the first two trimesters.
Sources
- “The Impact and Management of Fibroids for Fertility: An Evidence-Based Approach.”
- “The Rapid Growth of Fibroids During Early Pregnancy.”



